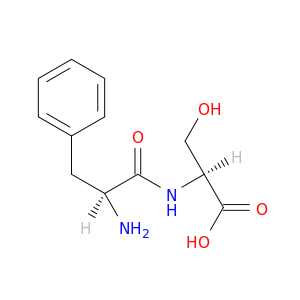
H-Phe-ser-oh
| Title | Journal |
|---|---|
| Affinity and translocation relationships via hPEPT1 of H-X aa-Ser-OH dipeptides: evaluation of H-Phe-Ser-OH as a pro-moiety for ibuprofen and benzoic acid prodrugs. | European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics : official journal of Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Pharmazeutische Verfahrenstechnik e.V 20110201 |
| L-Isoleucyl-L-serine 0.33-hydrate, L-phenylalanyl-L-serine and L-methionyl-L-serine 0.34-hydrate. | Acta crystallographica. Section C, Crystal structure communications 20060101 |
| Concentration-dependent atypical intestinal absorption of cyclic phenylalanylserine: small intestine acts as an interface between the body and ingested compounds. | Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin 20031101 |
| Concentration-dependent preferences of absorptive and excretive transport cause atypical intestinal absorption of cyclic phenylalanylserine: small intestine acts as an interface between the body and ingested compounds. | Research communications in molecular pathology and pharmacology 20020101 |