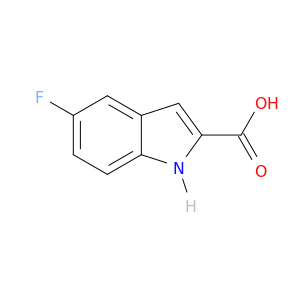
5-Fluoroindole-2-carboxylic acid
| Title | Journal |
|---|---|
| Thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one derivatives as PDK1 inhibitors discovered by fragment-based screening. | Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 20120615 |
| Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical phenotypes in Plasmodium falciparum. | Nature chemical biology 20091001 |
| Microsphere-based protease assays and screening application for lethal factor and factor Xa. | Cytometry. Part A : the journal of the International Society for Analytical Cytology 20060501 |
| Non-peptidic small-molecule inhibitors of the single-chain hepatitis C virus NS3 protease/NS4A cofactor complex discovered by structure-based NMR screening. | Journal of medicinal chemistry 20040506 |
| Sustained ER Ca2+ depletion suppresses protein synthesis and induces activation-enhanced cell death in mast cells. | The Journal of biological chemistry 20020419 |