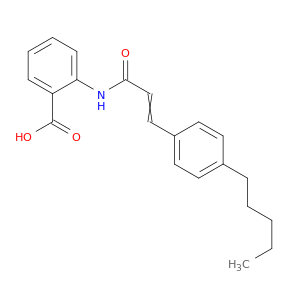
2-(3-(4-Pentylphenyl)acrylamido)benzoic acid
| Title | Journal |
|---|---|
| Diglycolic acid is the nephrotoxic metabolite in diethylene glycol poisoning inducing necrosis in human proximal tubule cells in vitro. | Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 20111101 |
| Inhibition of the calcium-activated chloride current in cardiac ventricular myocytes by N-(p-amylcinnamoyl)anthranilic acid (ACA). | Biochemical and biophysical research communications 20101119 |
| Inhibitors of TRP channels reveal stimulus-dependent differential activation of Ca2+ influx pathways in human neutrophil granulocytes. | Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's archives of pharmacology 20091201 |
| Acute action of rotenone on nigral dopaminergic neurons--involvement of reactive oxygen species and disruption of Ca2+ homeostasis. | The European journal of neuroscience 20091101 |
| H2O2-induced Ca2+ influx and its inhibition by N-(p-amylcinnamoyl) anthranilic acid in the beta-cells: involvement of TRPM2 channels. | Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 20090901 |
| Inhibition of the transient receptor potential cation channel TRPM2 by 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB). | British journal of pharmacology 20080301 |
| Phospholipase A2 is important for glucose induction of rhythmic Ca2+ signals in pancreatic beta cells. | Pancreas 20070801 |
| N-(p-amylcinnamoyl)anthranilic acid (ACA): a phospholipase A(2) inhibitor and TRP channel blocker. | Cardiovascular drug reviews 20070101 |
| Prostaglandin E2 release in gastric antral mucosa of guinea-pigs: basal PGE2 release by cyclo-oxygenase 2 and ACh-stimulated PGE2 release by cyclo-oxygenase 1. | Experimental physiology 20061101 |
| Inhibition of TRPM2 cation channels by N-(p-amylcinnamoyl)anthranilic acid. | British journal of pharmacology 20060601 |
| Enhancement of Ca2+-regulated exocytosis by indomethacin in guinea-pig antral mucous cells: arachidonic acid accumulation. | Experimental physiology 20060101 |
| Arachidonyltrifluoromethy ketone, a phospholipase A(2) antagonist, induces dispersal of both Golgi stack- and trans Golgi network-resident proteins throughout the cytoplasm. | Biochemical and biophysical research communications 20010223 |