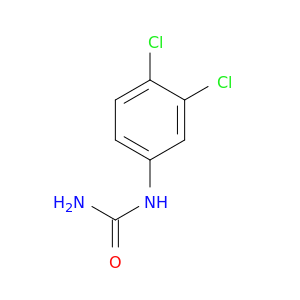
1-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)urea
| Title | Journal |
|---|---|
| Photocatalytic degradation of 3,4-dichlorophenylurea in aqueous gold nanoparticles-modified titanium dioxide suspension under simulated solar light. | Journal of hazardous materials 20110615 |
| Biotransformation and biomonitoring of phenylurea herbicide diuron. | Bioresource technology 20110201 |
| Diuron biotransformation and its effects on biofilm bacterial community structure. | Chemosphere 20101101 |
| QSAR-analysis and mixture toxicity as diagnostic tools: Influence of degradation on the toxicity and mode of action of diuron in algae and daphnids. | Aquatic toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 20100401 |
| An experimental design approach employing artificial neural networks for the determination of potential endocrine disruptors in food using matrix solid-phase dispersion. | Journal of chromatography. A 20090227 |
| Leaching of Diuron, Linuron and their main metabolites in undisturbed field lysimeters. | Journal of environmental science and health. Part. B, Pesticides, food contaminants, and agricultural wastes 20090101 |
| The environmental fate of diuron under a conventional production regime in a sugarcane farm during the plant cane phase. | Pest management science 20080901 |
| Measurement uncertainty arising from trueness of the analysis of two endocrine disruptors and their metabolites in environmental samples. Part I: ultrasonic extraction from diverse sediment matrices. | Journal of chromatography. A 20070406 |
| Leaching potential of some phenylureas and their main metabolites through laboratory studies. | Environmental science and pollution research international 20061001 |
| Some chemical contaminant of surface sediments at the Baltic Sea coastal region with special emphasis on androgenic and anti-androgenic compounds. | Journal of environmental science and health. Part A, Toxic/hazardous substances & environmental engineering 20060101 |
| A field study to assess the degradation and transport of diuron and its metabolites in a calcareous soil. | The Science of the total environment 20021007 |
| Antifouling paint booster biocides in UK coastal waters: inputs, occurrence and environmental fate. | The Science of the total environment 20020703 |
| Determination of antifouling pesticides and their degradation products in marine sediments by means of ultrasonic extraction and HPLC-APCI-MS. | Fresenius' journal of analytical chemistry 20010801 |
| Degradation products of a phenylurea herbicide, diuron: synthesis, ecotoxicity, and biotransformation. | Environmental toxicology and chemistry 20010701 |