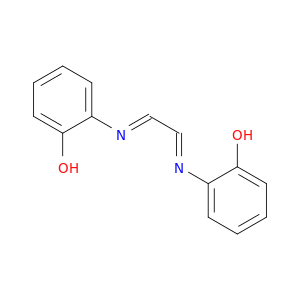
Glyoxalbis(2-hydroxyanil)
| Title | Journal |
|---|---|
| A new mouse model for the slow-channel congenital myasthenic syndrome induced by the AChR εL221F mutation. | Neurobiology of disease 20120301 |
| High-density areas on muscle CT in childhood-onset Pompe disease are caused by excess calcium accumulation. | Acta neuropathologica 20101001 |
| Regulation of pH During Amelogenesis. | Calcified tissue international 20100201 |
| Chromium(III) determination without sample treatment by batch and flow injection potentiometry. | Analytica chimica acta 20090216 |
| Electronic structure of the glyoxalbis(2-hydroxyanil) (gha) ligand in [Co(III)(gha)(PPh3)2]+: radical vs. non-radical states. | Dalton transactions (Cambridge, England : 2003) 20080714 |
| Ancillary ligand determination of the spin location in both oxidised and reduced forms of diruthenium complexes bridged by bis-bidentate 1,4-bis(2-phenolato)-1,4-diazabutadiene. | Dalton transactions (Cambridge, England : 2003) 20070521 |
| Proteolysis on maturing enamel surface, as shown by gel-coating methods. | European journal of oral sciences 20060501 |
| A new coordination mode of the photometric reagent glyoxalbis(2-hydroxyanil) (H2gbha): bis-bidentate bridging by gbha2- in the redox series [(mu-gbha)[Ru(acac)2]2]n (n = -2, -1, 0, +1, +2), including a radical-bridged diruthenium(III) and a Ru(III)/Ru(IV) intermediate. | Inorganic chemistry 20051128 |
| Focal caspase activation underlies the endplate myopathy in slow-channel syndrome. | Annals of neurology 20040301 |
| Chromium(III) ion selective electrode based on glyoxal bis(2-hydroxyanil). | Talanta 20030704 |
| Altered pH regulation during enamel development in the cystic fibrosis mouse incisor. | Journal of dental research 20030501 |
| Synthesis, crystal structure, spectral studies, and catechol oxidase activity of trigonal bipyramidal Cu(II) complexes derived from a tetradentate diamide bisbenzimidazole ligand. | Inorganic chemistry 20010226 |